Given the following picture of a linked list, where head, P and Q are of type LLNode<String>:
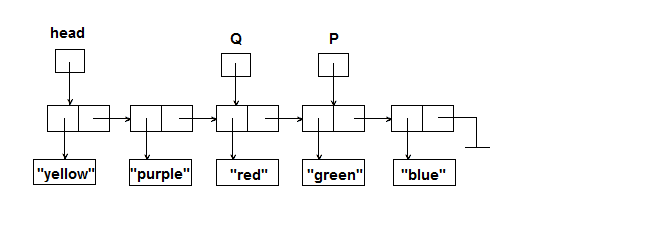
Write the code that will manipulate the linked list as follows. Each question should use the original list shown above.
- Make P point to the node containing the String "purple".
- Make Q point to the node containing the String "green".
- Make P point to the node containing the String "red".
- Make the node containing the String "green" point to the node containing the String "red".
- Make the node containing the String "purple" point to the node containing the String "green".
- Make the node containing the String "red" point to the node containing the String "purple".
- Concatenate the element field in the node P points to and the element field in the node Q points to and store the result in the node that currently contains "purple".
- Remove the node containing "blue" from the list.
- Remove the node containing "green" from the list.
Given the following linked list, where P, Q and S are of type LLNode<String>:
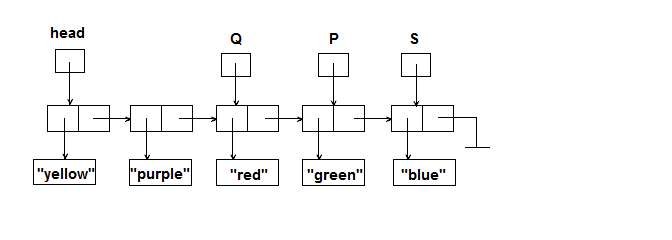
Show how each of the following statements changes the linked list. Draw a similar diagram and show the resulting list. Each question should be answered starting with the original list shown above.
- S.setInfo(P.getInfo());
- P.setInfo(head.getInfo() + Q.getInfo());
- S = Q.getLink();
- P.setLink(head);
- head.setLink(Q.getLink());
- Q = S.getLink();
- Q = Q.getLink();
- P.setLink(P);
a. p = new LLNode<String>(" ");
p.setInfo("10");
q = new LLNode<String>(" ");
q.setInfo("15");
q.setLink(p);
p = new LLNode<String>(" ");
p.setInfo(q.getInfo());
System.out.println(p.getInfo() + " " + q.getInfo()
+ " " + q.getLink().getInfo());
b. p = new LLNode<String>("yes");
p.setLink(new LLNode<String>("no"));
q = p.getLink();
q.setLink(null);
p.setInfo("5");
q.setInfo("10");
r = new LLNode<String>("maybe");
q.setLink(r);
q.setInfo(r.getInfo());
r.setInfo(p.getInfo());
System.out.println(r.getInfo() + " " + q.getInfo()
+ " " + p.getInfo());